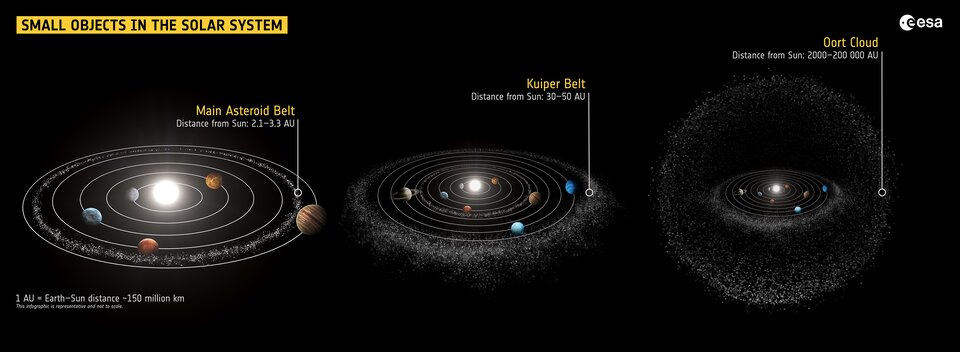
The solar system consists of one star, eight planets, five dwarf planets, hundreds of moons, thousands of comets, and more than a million asteroids. As of the latest statistics. In this post, we are going to cover everything you need to know about its astonishing mysteries.
The solar system is located in a small partial arm of the Milky Way, called the Orion Arm. Our solar system orbits the center of the galaxy at about 515,000 mph (828,000 kph), taking about 230 million years to complete one orbit around the galactic center.
It is called the solar system, because it has a star in the center, which is the Sun, and everything else orbits around it, due to gravity.
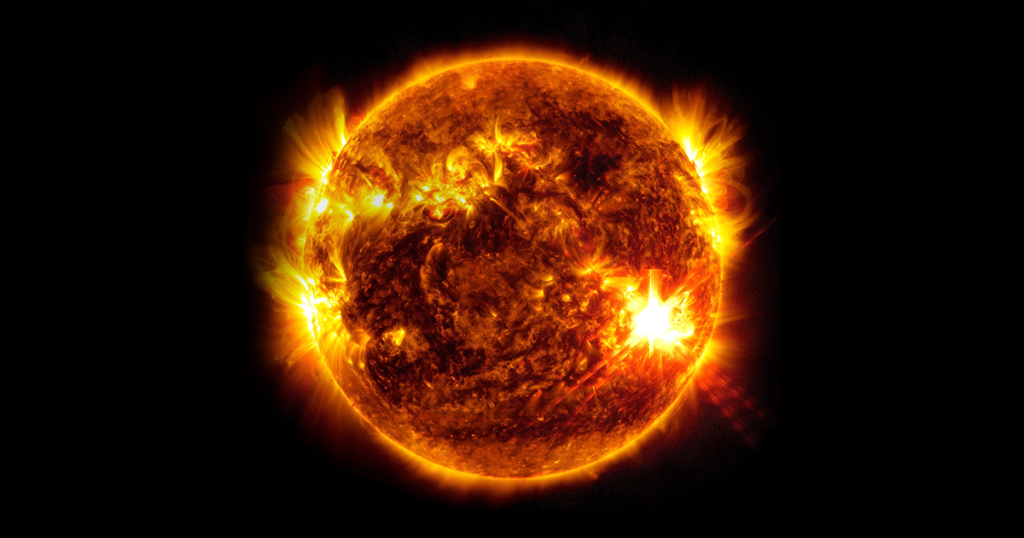
Star
We only have one star in our solar system. This star has so much mass that all objects, including our planet, orbit around this giant. This star is called Sun.
The Sun
The Sun is the largest and heaviest object in the solar system, for that reason all the planets and satellites on the solar system orbit around it. It has a diameter of approximately 1,391,000 km (864,000 miles), which is about 109 times the diameter of Earth. Also it has a mass of approximately 1.989×1030 kg, which is about 333,000 times the mass of Earth.

Planets
There are 8 planets in the solar system. If you are interested in checking the differences between each planet, I have created a planet comparison tool just for this.
Mercury
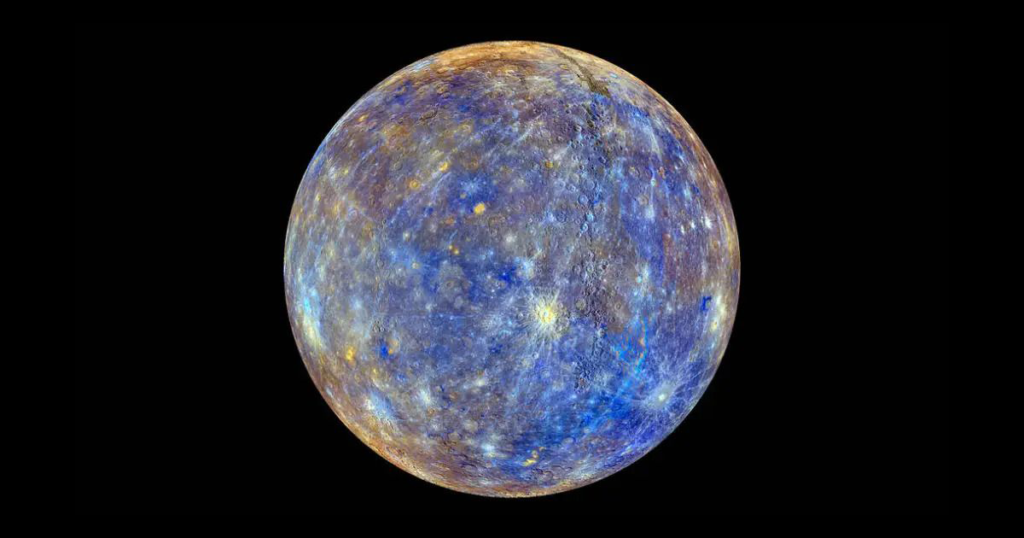
Mercury is the first planet on the solar system, meaning it is the closest planet to the Sun, but it’s not the hottest. What makes it fascinating is how extreme it is: it’s the smallest planet in the Solar System, it has no moons, and its surface is covered in craters like our Moon. A single day on Mercury lasts almost two months on Earth, and temperatures swing wildly between scorching heat and freezing cold.

Venus
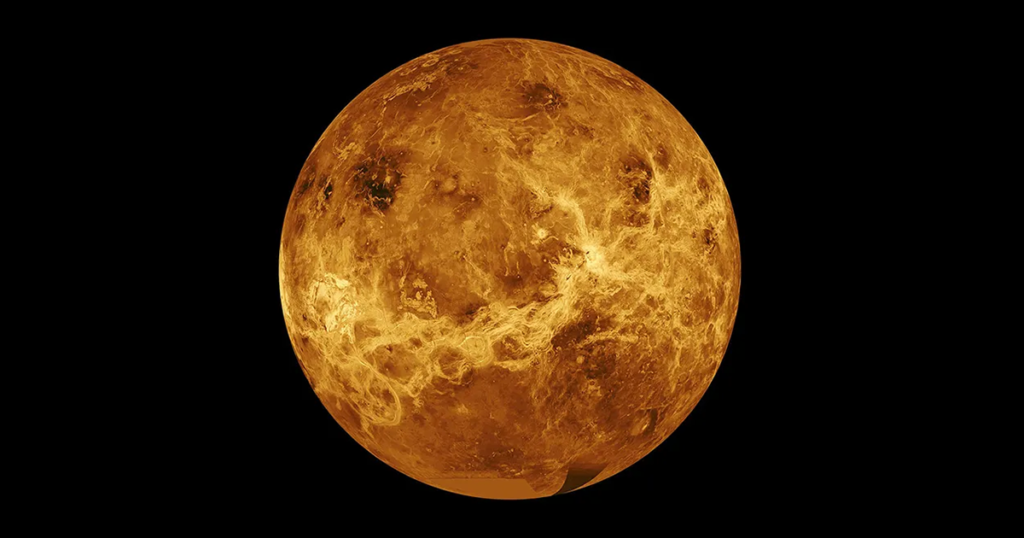
Venus is the second planet from the Sun and is often called Earth’s twin because of its similar size. But don’t let that fool you. Venus is the hottest planet in the Solar System. Its thick atmosphere traps heat so well that it becomes even hotter than Mercury, the planet closest to the Sun. The surface is hidden beneath clouds of toxic gas, and interestingly, a single day on Venus lasts longer than an entire year.

Earth
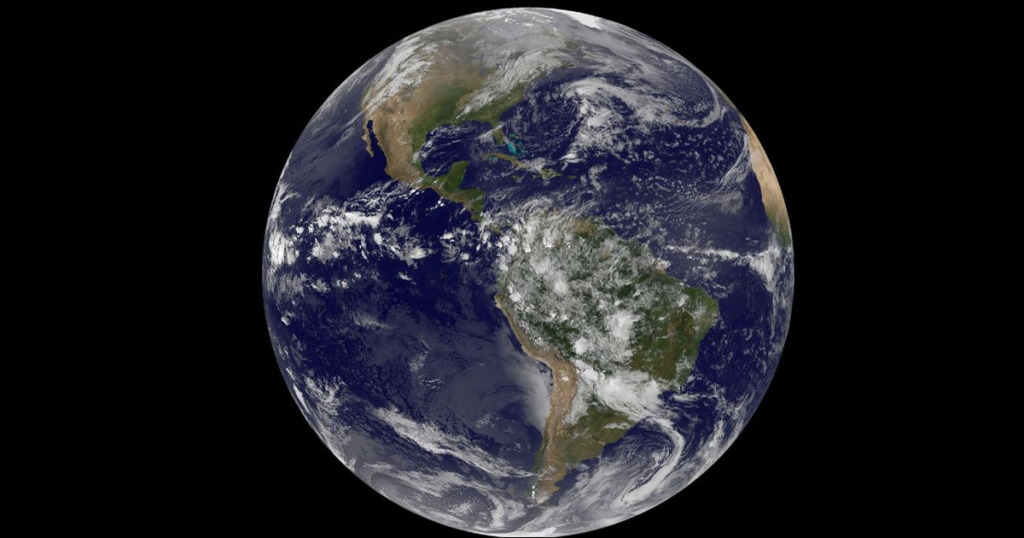
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only one known to support life. It has a perfect mix of atmosphere, temperature, and water that makes life possible. About 70% of its surface is covered in oceans, and it has one natural satellite, the Moon. Earth also has seasons, weather, and a protective magnetic field that shields it from harmful space radiation.

Mars
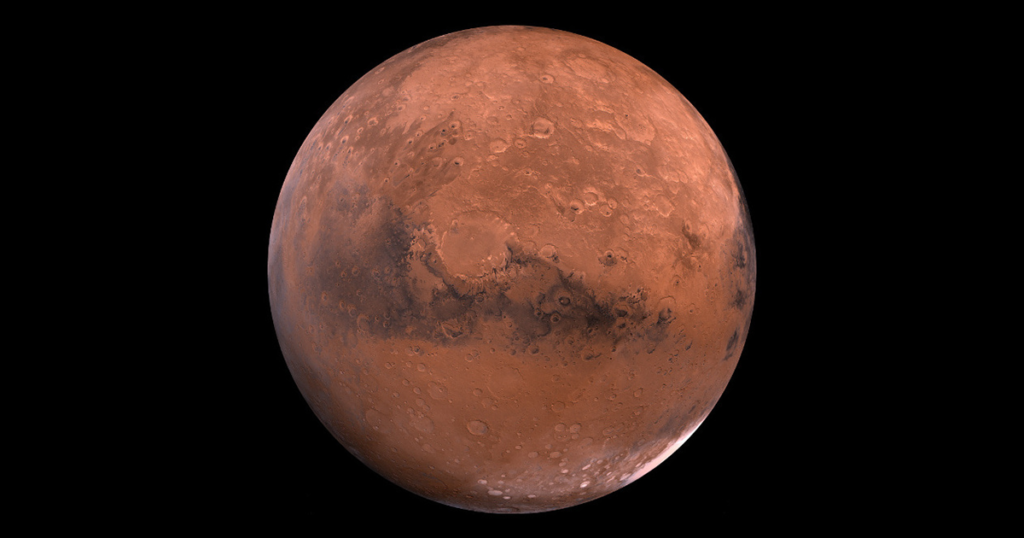
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and is often called the Red Planet because of its rusty surface. It has the largest volcano and canyon in the Solar System, and scientists believe it once had water. Mars is much colder than Earth and has two small moons. It’s one of the most explored planets, with many missions searching for signs of past life.

Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It’s a gas giant, meaning it doesn’t have a solid surface like Earth. One of its most famous features is the Great Red Spot, a giant storm that has been raging for centuries. Jupiter has dozens of moons, including Ganymede, the largest moon in the Solar System.
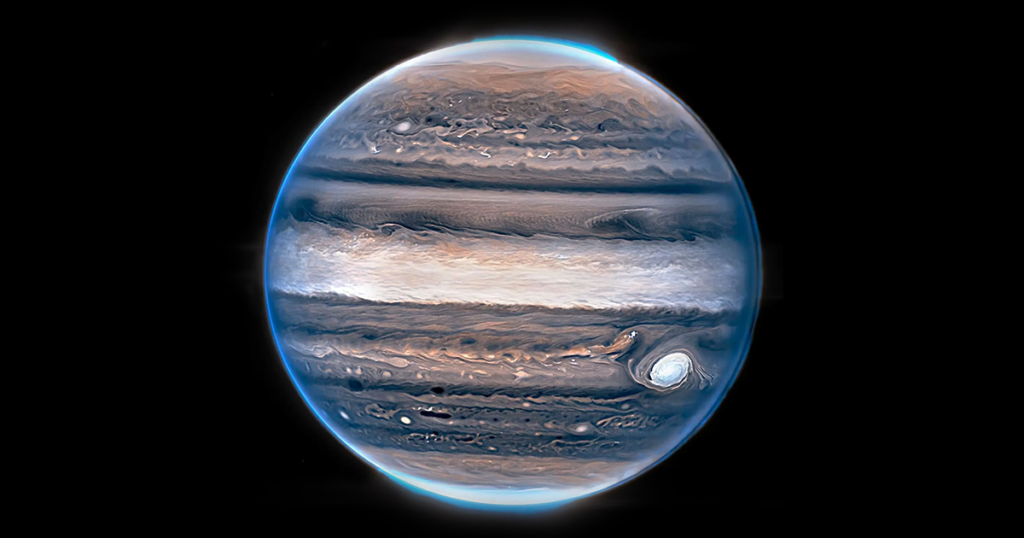

Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and is best known for its stunning rings. These rings are made of ice and rock and stretch wide around the planet. Like Jupiter, Saturn is a gas giant and doesn’t have a solid surface. It also has many moons, and some of them may have oceans beneath their icy crusts.
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun and has a pale blue color because of the gas methane in its atmosphere. What makes Uranus unique is that it spins on its side, making its seasons last for years. It’s an ice giant with faint rings and more than 25 moons.
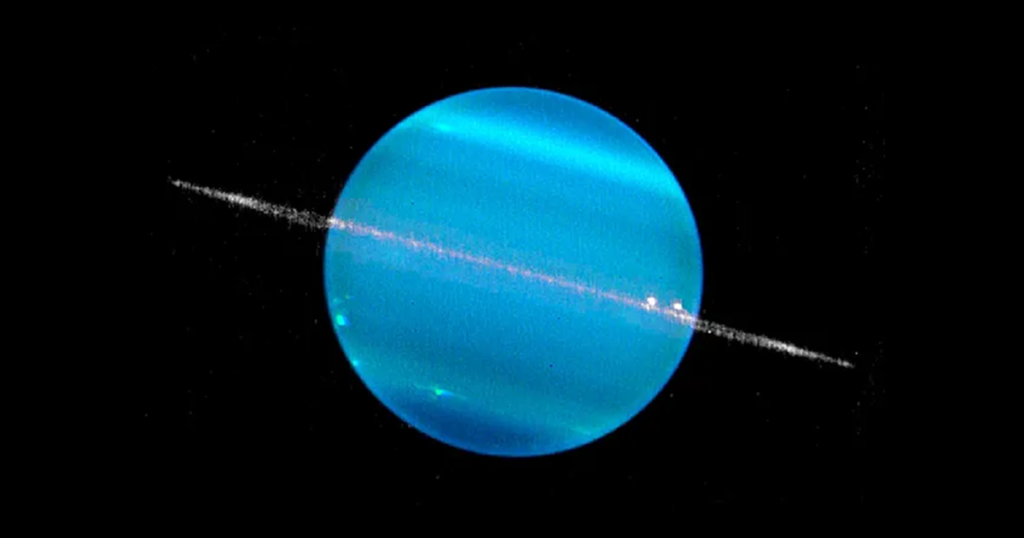

Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun. It’s deep blue in color and has the strongest winds in the Solar System, reaching speeds faster than any hurricane on Earth. Like Uranus, Neptune is an ice giant and has a cold, stormy atmosphere with many moons orbiting it.
Dwarf planets
There are 5 dwarf planets in the solar system.
A dwarf planet is an object that orbits the Sun, and has sufficient mass to have an almost perfect round shape, just like any other planet, the key relies on the difference of orbital dominance. While planets has cleared its orbit of other debris, dwarf planets have not.
Ceres
Ceres is the only dwarf planet located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Discovered in 1801, it was once considered a planet and later an asteroid. It is named after the ancient Roman goddess of agriculture.
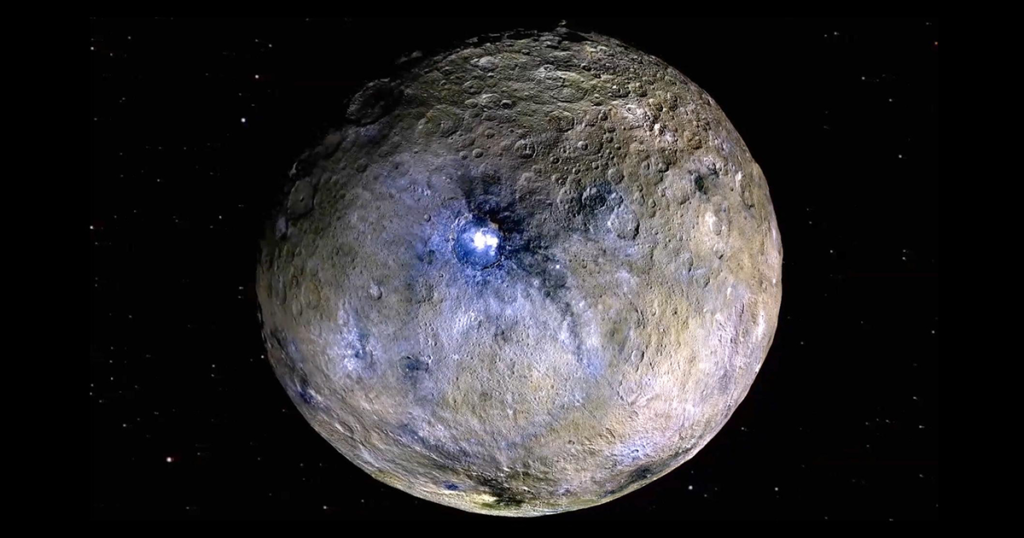

Pluto
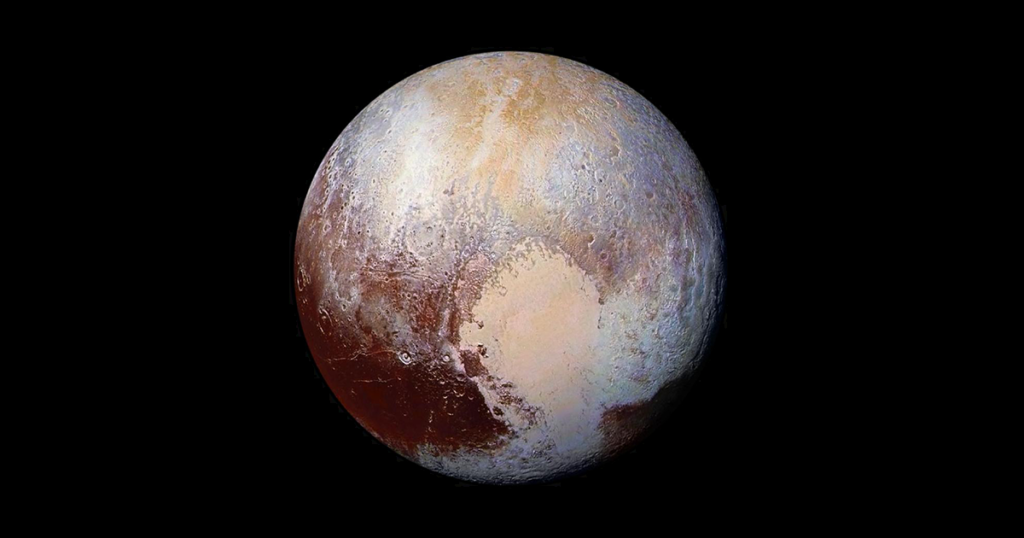
Pluto was long considered the ninth planet until it was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006. It orbits in the Kuiper Belt and is named after the Roman god of the underworld. It was discovered in 1930 and remains one of the most well-known dwarf planets.

Eris
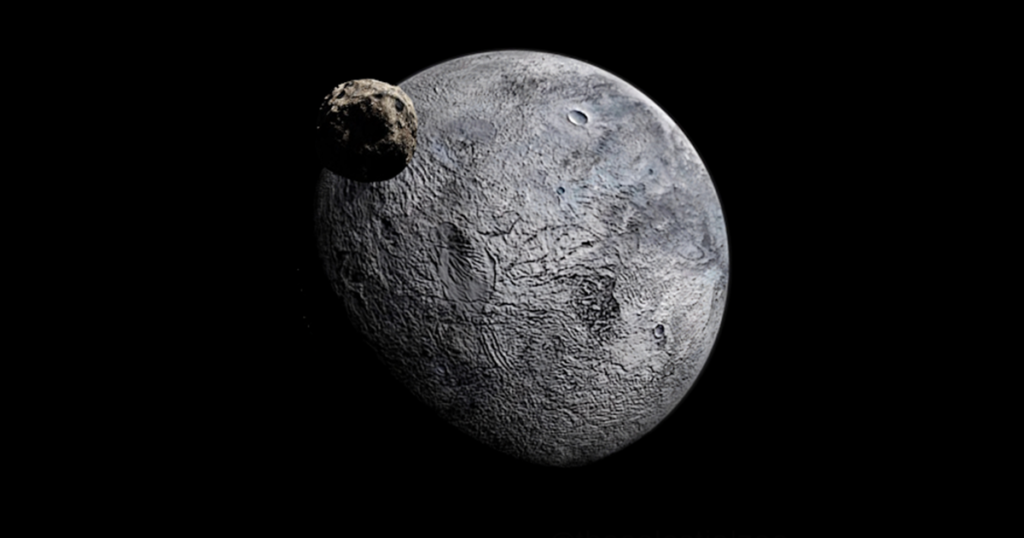
Eris, discovered in 2005, is slightly smaller than Pluto but has more mass. It is located in the Kuiper Belt and is one of the most distant known objects in the Solar System. Eris is named after the Greek goddess of chaos and strife.

Makemake
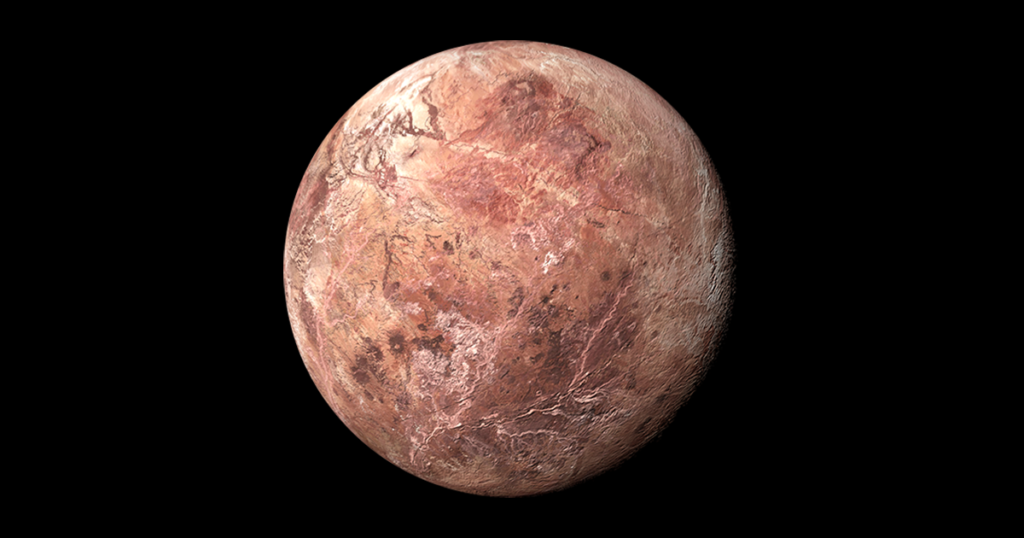
Makemake, also in the Kuiper Belt, was discovered in 2005. It has a very bright surface covered in ice and is named after a deity of fertility and creation from the Rapa Nui mythology of Easter Island.

Haumea
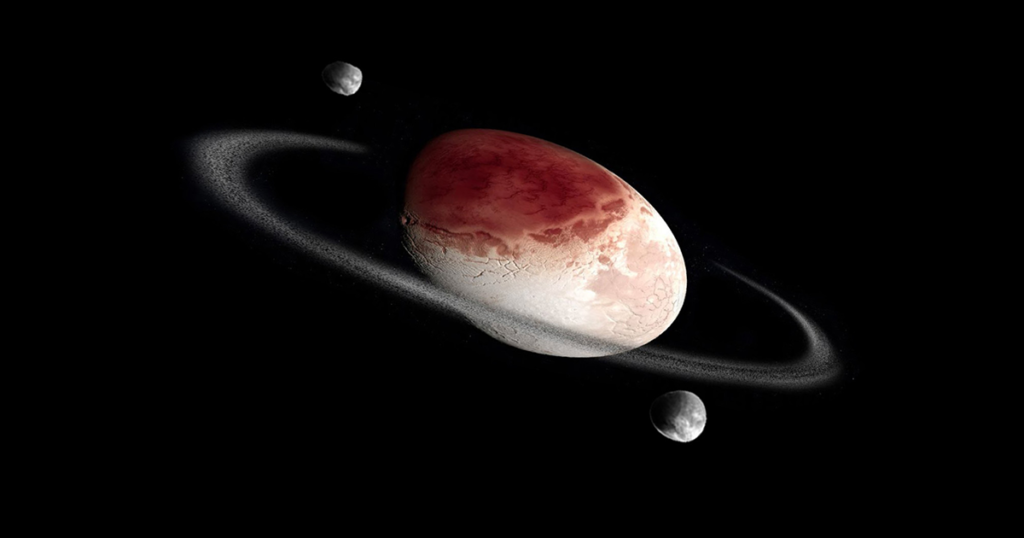
Haumea is known for its unusual, stretched shape and incredibly fast rotation, making it one of the fastest-spinning large objects in the Solar System. Also located in the Kuiper Belt, Haumea is named after the Hawaiian goddess of childbirth.

Moons
There are 288 planetary moons in the solar system.
Most planets in our solar system have moons, but not all, Mercury and Venus have none. The moon that orbits around our planet, Earth, we have named it Moon. But each moon has its own name.
Mercury: 0 moons
Venus: 0 moons
Earth: 1 moon
Mars: 2 moons (Phobos and Deimos)
Jupiter: 95 moons (including the four large Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto)
Saturn: 146 moons (including the largest moon, Titan)
Uranus: 27 moons (with the largest being Titania, Oberon, Umbriel, Ariel, and Miranda)
Neptune: 14 moons (the largest being Triton)
Comets
There are more than 3,900 known comets in our Solar System, but scientists believe that this is just a small fraction of the total. Some estimates suggest that there could be over a trillion comets orbiting the Sun, especially in distant regions like the Oort Cloud and the Kuiper Belt.
Comets are icy objects that release gas and dust when they get close to the Sun, forming a glowing head called a coma and often a long, bright tail that points away from the Sun. These tails can stretch for millions of kilometers and are one of the most spectacular sights in the night sky. Comets are thought to be some of the most primitive bodies in the Solar System, containing materials left over from its formation more than 4.6 billion years ago.
They follow long, elliptical orbits that can take them far beyond the outer planets before returning toward the Sun. Some visit us regularly, like Halley’s Comet, which appears roughly every 76 years, while others pass by once and never return.
Asteroids
There are more than 1.3 million known asteroids in our Solar System, and the real number could be much higher. These rocky objects are remnants from the early formation of the planets, making them some of the oldest pieces of the Solar System. Unlike comets, asteroids are made mostly of rock and metal and do not have tails.
Most asteroids orbit the Sun within three main regions: the Main Asteroid Belt, located between Mars and Jupiter, is the largest and most populated zone. Then there’s the Kuiper Belt, beyond Neptune, where icy asteroids mix with dwarf planets and comets. Lastly, the Oort Cloud is a distant, spherical shell of icy objects that may also include asteroid-like bodies, although it remains largely theoretical due to its distance.
Some asteroids are only a few meters wide, while others, like Ceres, are hundreds of kilometers across. A few even have their own moons. Because of their proximity to Earth and potential impact risks, many asteroids are closely monitored as Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) by space agencies around the world.