Neptune is the furthest away planet of the 8 that make our solar system.
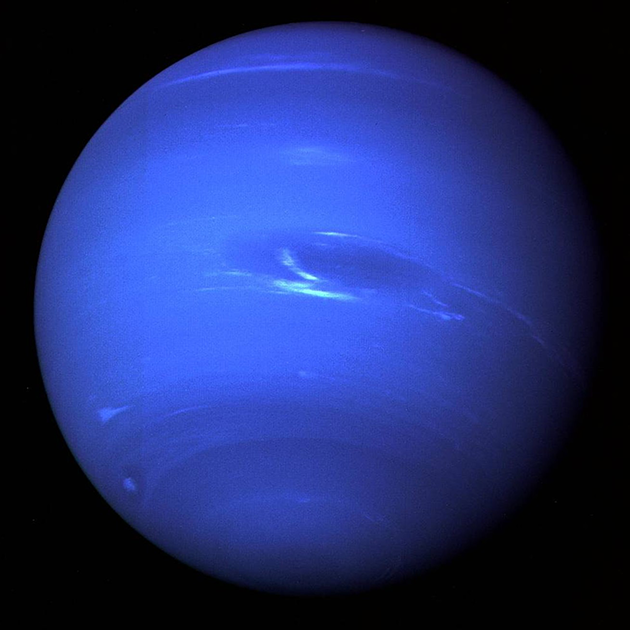
Table of Contents
Remarkable data about Neptune:
| Radius | 24,622 km |
| Mass | 1.024 × 10^26 kg |
| Gravity | 11.15 m/s² |
| Distance from Sun | 4.495 billion km |
| Age | 4.503 billion years |
| Orbital period | 165 years |
| Natural satellites | 14 Triton, Proteus, Nereid, Larissa, Galatea, Despina, Thalassa, Naiad, Halimede, Psamathe, Sao, Laomedeia, Neso, Hippocamp |
Key Features of Neptune:
- Color and Atmosphere: it is famous for its striking blue color, which is due to the presence of methane in its atmosphere. The methane absorbs red light and reflects blue light, giving the planet its vivid hue.
- Great Dark Spot: Similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, it has a large storm system called the Great Dark Spot. This feature, however, is not permanent and has been observed to change over time.
- Strong Winds: it is one of the windiest planets in our Solar System, with wind speeds reaching up to 1,500 miles per hour (2,400 kilometers per hour). These high-speed winds contribute to the dynamic and turbulent nature of its atmosphere.
- Ring System: it has a system of rings, though they are faint and less conspicuous compared to the rings of Saturn. The rings are composed mainly of dark, icy particles and are thought to be relatively young.
- Magnetic Field: it has a strong magnetic field that is tilted relative to its rotational axis. This magnetic field is complex and likely generated by the movement of conductive fluids within its interior.
Neptune’s Position in the Solar System:
- Orbit: it orbits the Sun at an average distance of about 2.7 billion miles (4.3 billion kilometers), which makes it have really low temperature, ranging around -225 °C.
- Rotation and Tilt: it rotates on its axis once every 16 hours, creating day and night. The planet is tilted at about 28 degrees, which leads to the changing seasons, which each last for more than 40 years.
